Description
Though being a global phenomenon, nowhere else in the world is climate change expected to have ecological, economic and social consequences as dramatic as those in the Mediterranean basin. Higher than average projected changes in climate and shifting weather patterns endanger an extremely rich and intertwined biological diversity, which supports human activities such as farming. In this context, the agriculture sector in particular is especially threatened, as it is largely climate-driven and thus highly vulnerable to its variability.
The risk of crop failure and pest damage, as well as natural hazards such as heat waves, storms or floods is likely to increase, requiring immediate action to be undertaken to adapt to this uncertain outlook.
The challenge is to develop tools to build more resilient, efficient and sustainable agriculture and food systems. To that end, the development of climate services to support decision-making and best practice in agriculture is essential.
That is why the aim of MED-GOLD is to translate state-of-the-art climate data and climate predictions — at the seasonal timescale and beyond — into easily accessible, valuable information for a wide range of end-users in the agriculture sector.
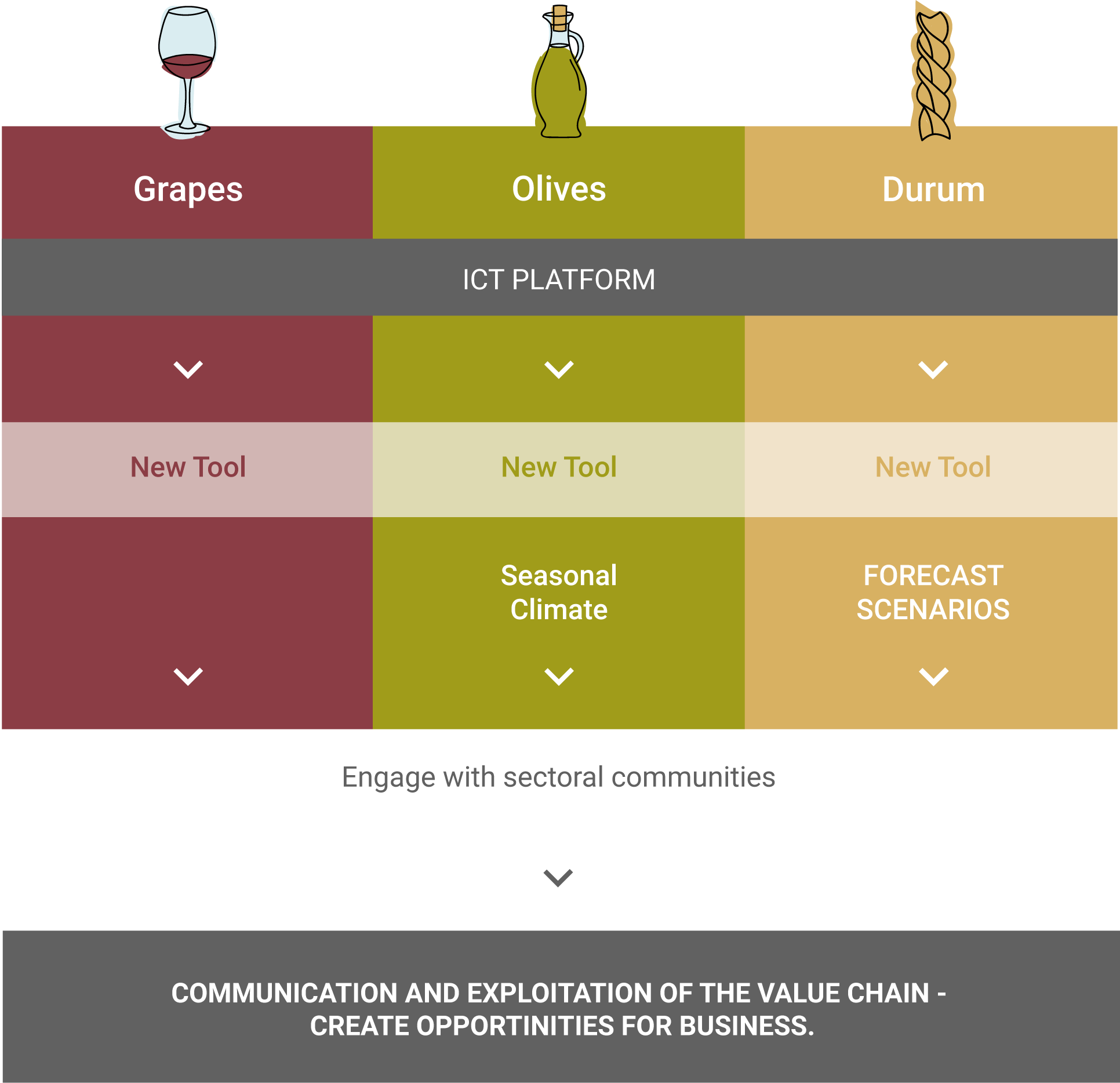
Though a reasonable amount of climate-related data is already widely accessible, their use for the management of climate-related risks is still limited. As such, it is a priority – in Europe and worldwide – to demonstrate the proof-of-concept for climate services in agriculture. To this end, MED-GOLD will build pilot climate services focusing on three key crops of the Mediterranean area: grapes, olives and durum wheat. These three crops – and their related food products, wine, oil, and pasta respectively – were chosen as case studies owing to their high ecological, economic, and cultural relevance to the Mediterranean region in particular, but also in Europe and worldwide.
These climate services – tailored to the end-users needs – will be co-designed by a consortium of the most relevant producers and stakeholders in the three sectors. These services will pave the way for a new replicable framework, with the aim of extending its applicability beyond the case studies considered for the project. For example, the replicability of the MED-GOLD methodology will be tested for coffee, another important global agricultural commodities.
The MED-GOLD objectives are summarised in the following list:
1_ To co-design, co-develop, test and assess the added value of proof-of-concept climate services for olive, grape and durum wheat
2_ To refine, validate and upscale the three pilot services with the wider European and global user communities for olive, grape and durum wheat
3_ To ensure replicability of MED-GOLD climate services in other crops/climate (e.g. coffee) and to establish link to polish making globally
4_ To implement a comprehensive communication and commercialization plan for MED-GOLD climate services to enhance market uptake
5_ To build better informed and connected end-user communities for the global olive oil, wine and pasta food systems and related policy making
Climate services
Within the European Commission (EC), the field of climate services has been identified as one of the few “flagship initiatives” of key areas of public interest in which to invest with priority during Horizon 2020.
In this context, the term ‘climate services’ has a broad meaning: transforming climate-related data and other information into customized products such as projections, trends, economic analysis, advice on best practices, development and evaluation of solutions, and any other climate-related service liable to benefit that may be of use for the society at large. These services include data, information and knowledge that support adaptation, mitigation and disaster risk management.MED-GOLD will provide climate services for grape, olives and durum wheat. The new services will be the result of the upgrading, tailoring and integration of existing modelling platforms. Innovative tools will be developed for the management of risks associated with the spread of noxious organisms, yield and quality losses and other climate related threats for farming crops. Importantly, these services will offer support for decision making at two different timescales: a shorter (seasonal) one, as well as a longer outlook over the next few decades.
All the new tools will be gathered into a single data interface platform for maximizing accessibility and ease of use for the end-users, as well as to generate synergies that can be reaped from common issues shared by the three agriculture sectors.
After various assessments and consultations, the expert group produced a document in which an analysis of projects funded by the EU in the field of climate services was provided, alongside the identification of the main challenges that require sustained research and innovation funding in order to build a successful, supportive market for climate services. The pinpointed challenge areas deal with:
– Enabling market growth
– Building the market framework
– Enhancing the quality and relevance of climate services
In turn, these areas are subdivided into nine main activities and 25 specific actions, the collection of which forms the roadmap itself.
According to the document, “Climate services have the potential to become the intelligence behind the transition to a climate-resilient and low-carbon society”.
You can find out how in the report here.
– There should be constant interaction with the users during all the phases of the development of a climate service
– This interaction should allow for the possibility of a change in the domain definition and scope of the services being developed
– A flexible management approach is best suited to effectively deal with users’ feedback
– Users may greatly benefit from the access to climate expertise during the development of the service
– The ultimate success of climate services requires the developers to be prepared to challenge the way in which users are involved in and interact with climate service projects.
Each of the suggestions above has been carefully taken into account during the planning of the MED-GOLD project, which includes former EUPORIAS partners and stakeholders in its consortium.
Workplan
Partners

BARILLA
BARILLA
It is an Italian food company producing pasta, sauces and bakery products.
placeholder
placeholder

BEETOBIT
BEETOBIT
An Italian ICT company focused on building scalable computing platforms for companies,
specialized in the planning, creation and maintenance of cloud-based systems.

BSC
BSC
The Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC) is the national supercomputing center in Spain, specializing in high performance computing.
placeholder

CNR
CNR
The largest public multidisciplinary research institution in Italy.
placeholder
placeholder

DCOOP
DCOOP
A Spanish food company, a cooperative of more than 75000 farmers and world’s largest producer of olive oil.
placeholder

EC2CE
EC2CE
A Spanish technological company that creates decision tools for the agricultural sector based on artificial intelligence prediction models.

ENEA
ENEA
The Italian government agency responsible for the areas of new technology, energy and sustainable economy.
placeholder

GMV
GMV
A technological business group which offers solutions, services and products in diverse range of sectors, including aerospace, defense and Earth Observation.

HORTA
HORTA
A university spin-off Italian company whose core activity is the development of Decision Support Systems for sustainable crop production based on ICT’s.

JRC
JRC
The Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission is the in-house science service of the Commission that provides evidence-based scientific and technical support to EU policies.

Met Office
Met Office
The UK’s national weather service. It makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change over the4 coming decades and centuries

NOA
NOA
The National Observatory of Athens (NOA) is the oldest research establishment in Greece. Its research activities span from the terrestrial interior, to atmospheric environment and space.

SOGRAPE
SOGRAPE
A Portuguese family-owned company, currently one of the strongest groups in the Iberian wine sector.
placeholder
placeholder

UMNG
UMNG
The Universidad Militar Nueva Granada (UMNG) is a Colombian public University ranked among the best universities in the country.
placeholder

UNIVLEEDS
UNIVLEEDS
The University of Leeds is one of the largest research-intensive universities in Britain, with world class centres of excellence that includes cross-cutting work on climate change and related topics.

UTH
UTH
The Networks and Telecommunications laboratory of the University of Thessaly, Greece, focuses on wireless networks, mobile communications and security of telecommunications.

